Data information knowledge wisdom
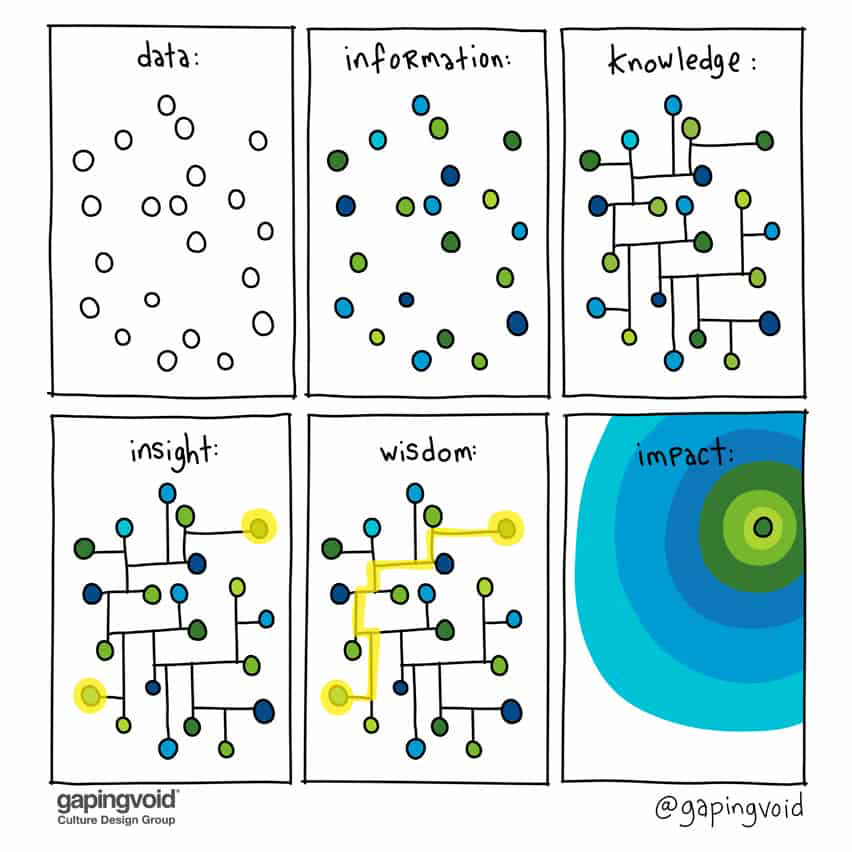
Data
- as fact
- as signal
- as symbol
Information
“Information is inferred from data” “Classically,” states a recent text, “information is mark: d as data that are endowed with meaning and purpose”
- Structural vs. functional
- Symbolic vs. subjective
Knowledge
“knowledge is mark: d with reference to information” “All knowledge is tacit” “Knowledge is a fluid mix of framed experience, values, contextual information, expert insight and grounded intuition that provides an environment and framework for evaluating and incorporating new experiences and information. It originates and is applied in the minds of knowers. In organizations it often becomes embedded not only in documents and repositories but also in organizational routines, processes, practices and norms.”
- as processed
- as procedural
- as propositional(命题)
Knowledge is a thought in the individual’s mind, which is characterized by the individual’s justifiable belief that it is true. It can be empirical and non-empirical, as in the case of logical and mathematical knowledge (e.g., “every triangle has three sides”), religious knowledge (e.g., “God exists”), philosophical knowledge (e.g., “Cogito ergo sum”), and the like. Note that knowledge is the content of a thought in the individual’s mind, which is characterized by the individual’s justifiable belief that it is true, while “knowing” is a state of mind which is characterized by the three conditions: (1) the individual believe[s] that it is true, (2) S/he can justify it, and (3) It is true, or it [appears] to be true
- subjective knowledge vs. subjective information
- subjective knowledge is characterized by justifiable belief, where subjective information is a type of knowledge concerning the meaning of data.
Wisdom
“the ability to make sound judgments and decisions apparently without thought”